Exploring and Researching the technologies of CMS
By Drashya Patel on 2024-11-20T23:08-05:00
Tags: No Tags
What is a CMS?
A Content Management System (CMS) is a software application that allows users to create, edit, and manage cotent on a website without needing the knowledge to code or technicatilies. There are various CMS such as Strapi, Ghost, Contentful, WordPress, Prismic, Sanity, etc.; With a CMS, someone can build a webpage from start, design it, edit it, organize the data and publish contents.
CMS platforms are important for:
- Work-Flow Automation: Builtin or third-party tools streamline publication and management.
- Content Organization: Easy to use interface for non-technial person, tagging, and searching of content.
- Multiplatform content distribution: After creating once share and distribute across different platforms like web, mobile.
- Decoupling: Headless CMS gives ability to developers to use modem frameworks such as react, vue etc.;
Ghost CMS
Ghost is a simple, open-source, and free CMS that is primarily used for blogging. It is created for writers and creators focusing on speed and performance. Ghost uses Node.js which helps in scalability and performance combined with Ghost.
Key features
- Simple and minimalistic interface: Easy to use and navigate.
- Membership and Subscription Support: Allows monetizing content via memberships.
- Node.js Backend: Ghost's backend runs on Node.js, offers non-blocking I/O operations, which makes it responsive and effective.
- Nunjucks Templating: Uses Nunjucks for rendering templates, enabling a straightforward way to structure page layouts.
Pros of Ghost CMS
- Efficient Performance: Node.js as backend make it very responsive, lightweight, and designed to handle concurrency with minimal resource usage.
- Self-Hosting option: Complete control over hosting environment and server configuration for advanced customizations.
- Free and Open-Source: No licensing fees, and the community contributes to its development and maintenance.
- Pre-Built SEO and Subscription Features: Developed for publishing, with built-in SEO and membership capabilities, reducing plugin dependency.
Cons of Ghost CMS
- Limited API Options: API support is minimal, making complex integrations harder.
- Less Flexible for Developers: Limited support for custom frontend frameworks, not completely headless.
- Node.js Knowledge Required: Self-hosting or custom development requires familiarity with Node.js and server management.
Implementation and Explaination
- "Connecting the ghost using content API"
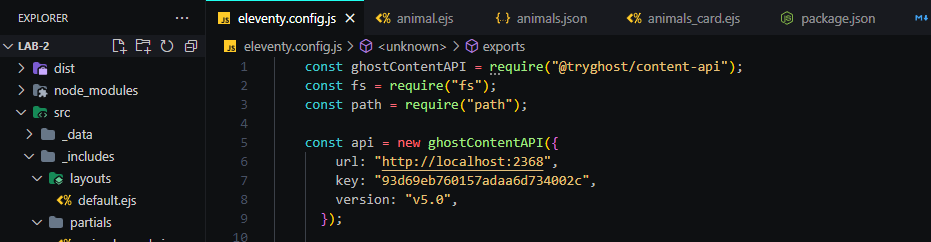
- "Adding the data to the page"
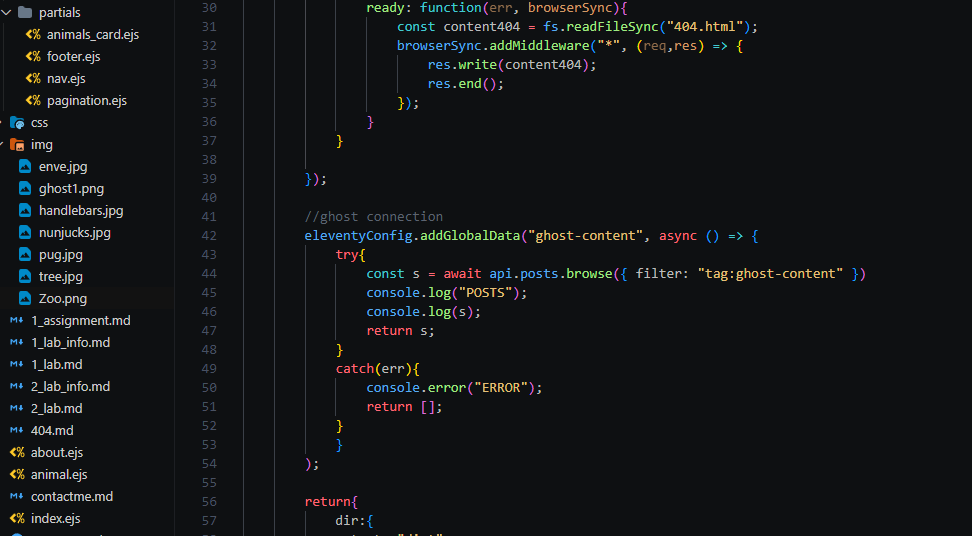
- "Getting the ghost data from post tag"
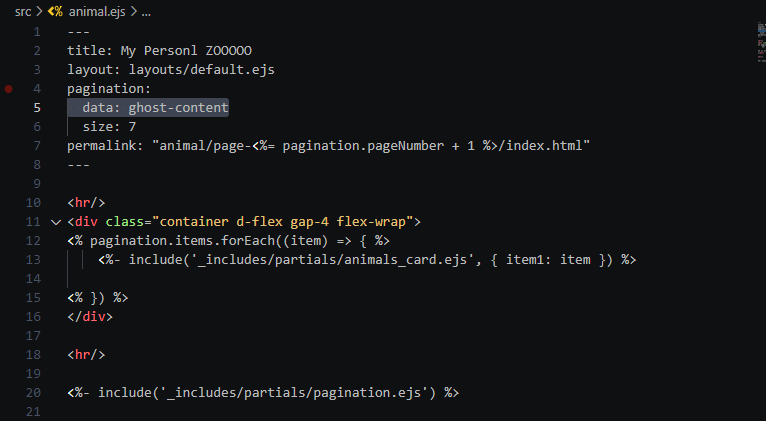
- "Getting the values from the post according to the data structure in ghost"
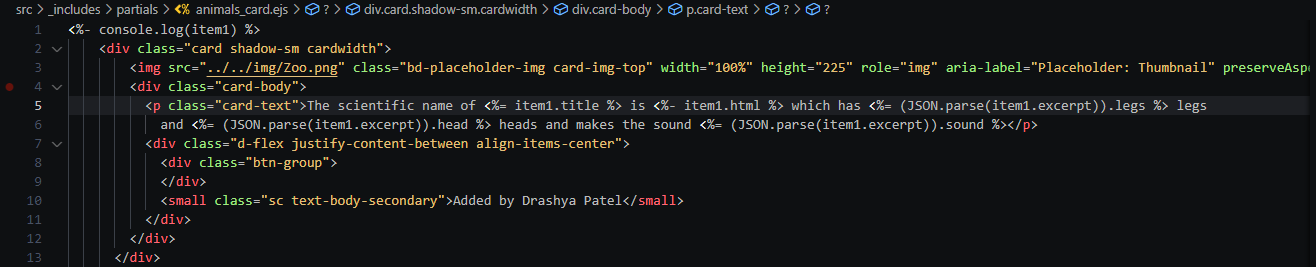
- "Blog posts added on the ghost cms."
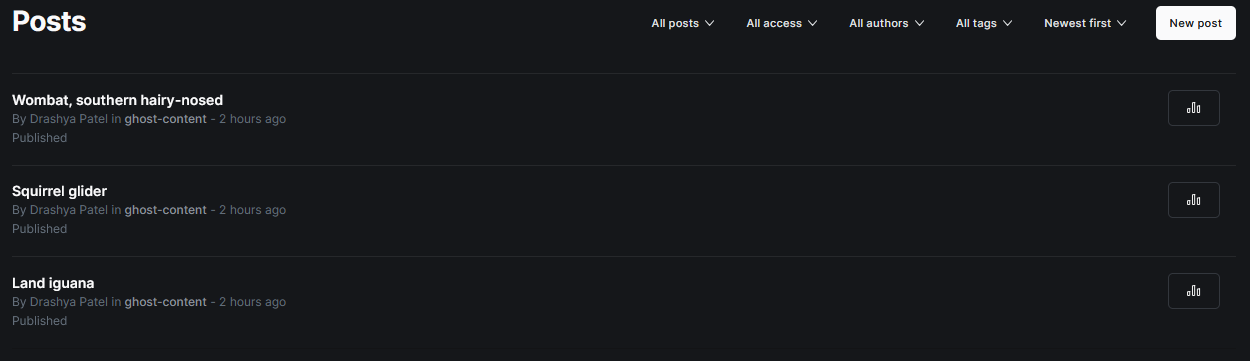
- "Each post with title, body and other content in excerpt. Also assigning each post a tag "ghost-content"



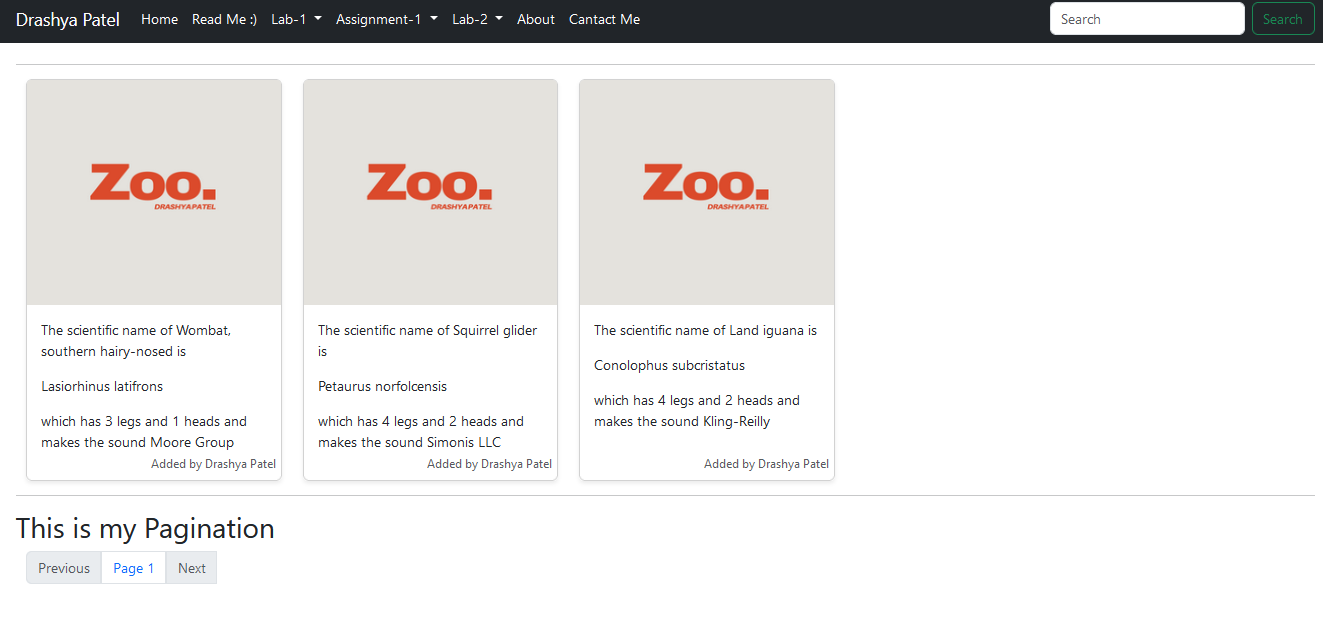
- This is how the Zoo page is looking, the content is from the posts on the ghost cms and not from .json. By the adding the posts on Ghost CMS, this page will fetch the added posts and display it accordingly.
Implementation video link
Contentful CMS
Contentful is a headless CMS with an API-firt design, which is focusing on content as a service. As a backend solution, Contentful prodivs complete control over where and how content is showed, with multi-platform compatibility, and supporting complex applications.
Key Features
- Headless CMS: API-first design, allowing developers to use any frontend framework. Allows developers to use any frontend stack such as React, Vue, Angular.
- Webhook Support: Enables seamless integration of CI/CD and other services. Also, enables automation of content deplyoment on the page workflow.
- API-First: Its primary interaction model is through APIs.
- Environment Support: Multiple environments for managing content in different lifecycle stages.
- Integrations and Extensibility: Straightforward and direct integrations with systems such as SHopify, Algolia, and AWS, while also allowign customized app development to increase the functionality.
- Content Modeling: Allows users to define custom content types and fields, creating a flexible and highly customizable data structure.
Contentful's API System
- REST API: Gives access to all the content data with strong query capabilities, designed for performance and flexibility.
- GraphQL API: Ideal for frontend frameworks, offering more efficient data retrieval, and reducing over-fetching.
- Management API: Enables programmable access to content management features, automating tasks like content creation, and update.
Pros of Contentful CMS
- API-First, headless design: Decoupling supports multi-platform usability, allowing advance forntend frameworks.
- Versioning Control and Environment Control: Development, staging, and production environments streamline release management and testing.
- Webhook and Integration Support: Native support for automation tools and integrations, creating a seamless content workflow.
Cons of Contentful CMS
- Expensive: Costs can escalate with high traffic or enterprise-level needs.
- Steep Learning Curve: Requires significant time and effort to master the platform and its features.
- No Native UI for Presentation: Lacks templating, so separate frontend is necessary for UI presentation.
Implementation and Explaination
- "Connecting the Contentful using content API and Space Token"
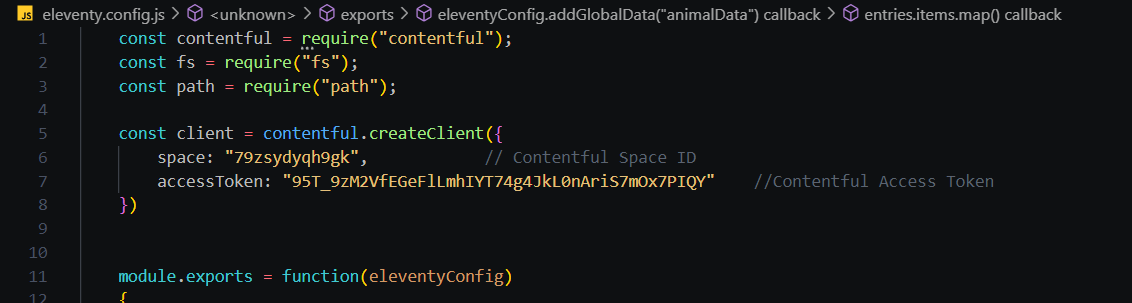
- "Adding the data to the page using the content type (animal) form the contentful ppost and fields using get entries function"
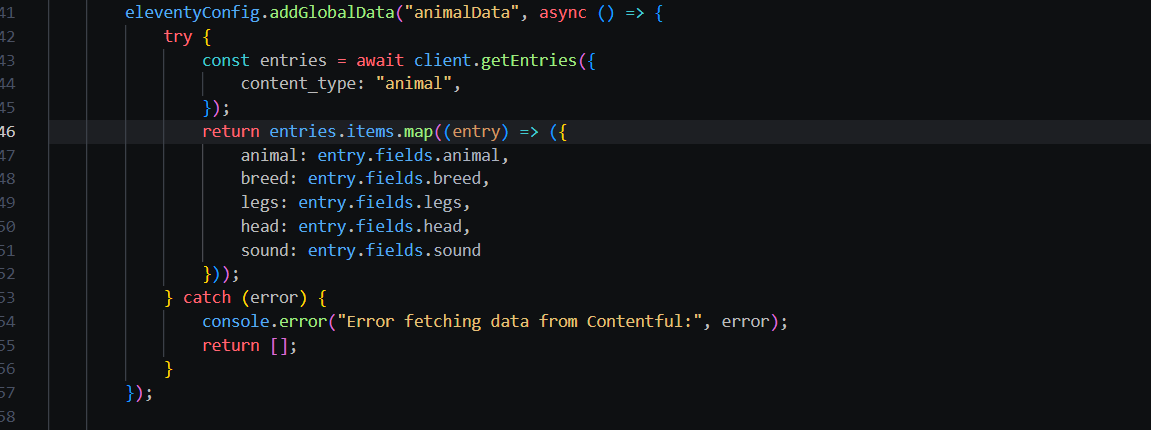
- "Getting the Contentful data from the custom content type using animalData key from GlobalData function."
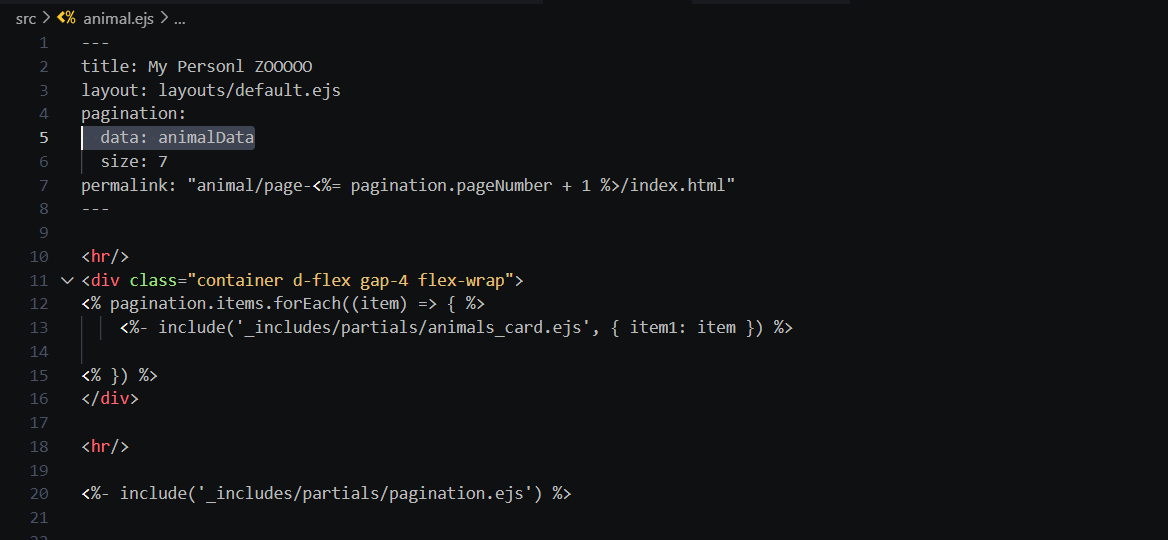
- "Now since we already made the content structure and field types acording to our animals.json data, there's no need to change anything the card part."
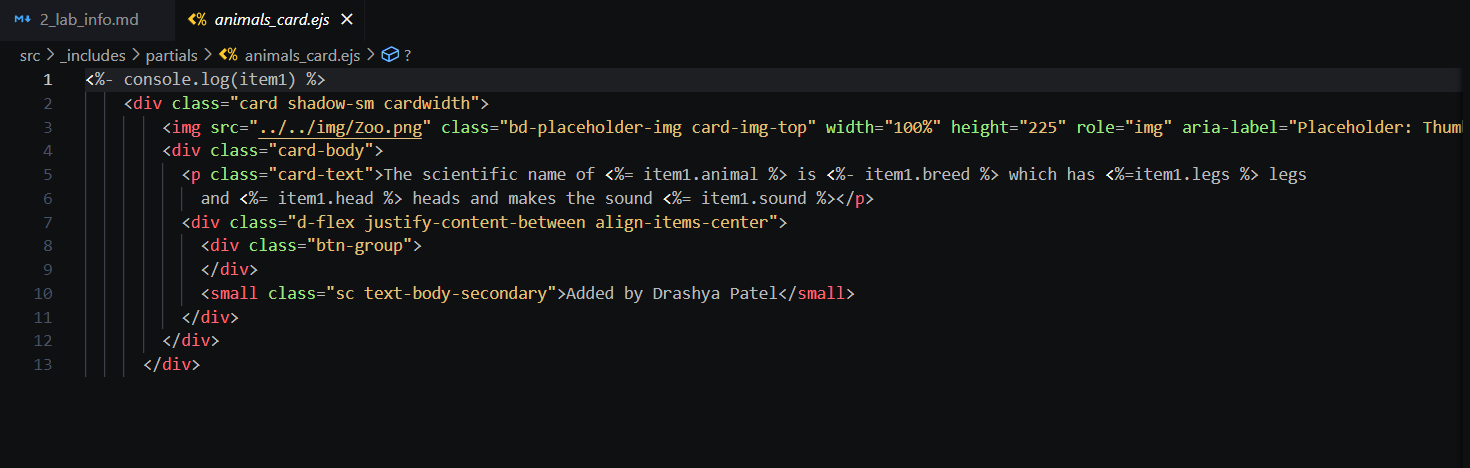
- "The custom content model created for the animal data."
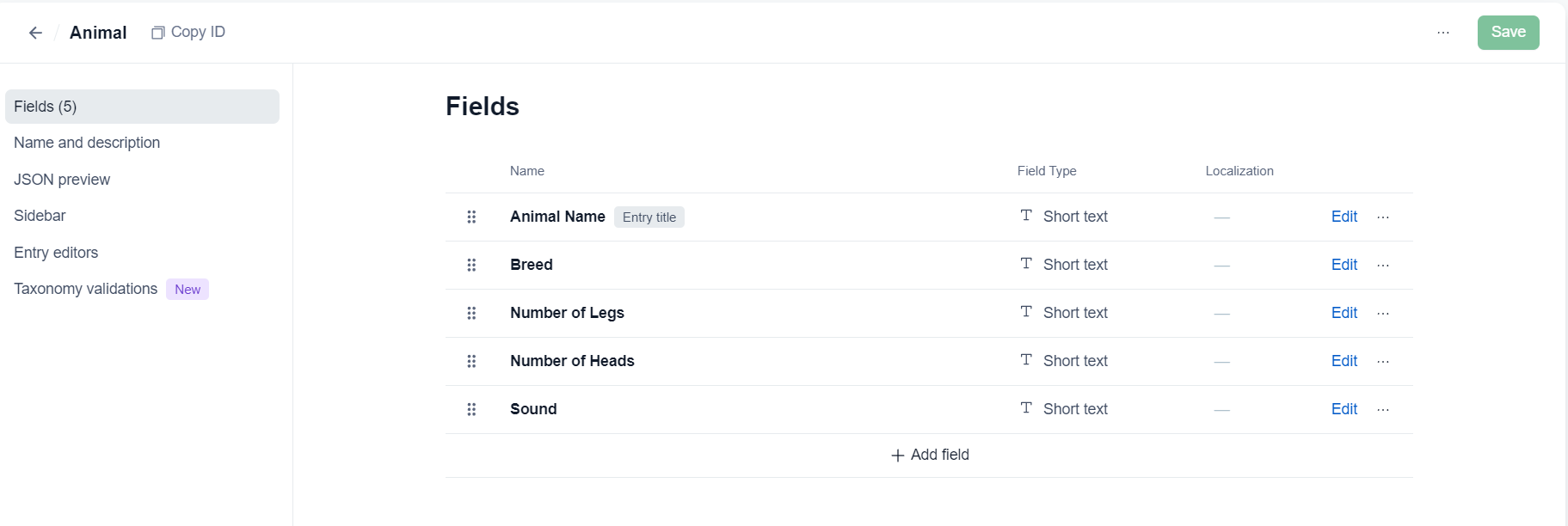
- "These are the custom fields created for the entries in the animal content model.(One of my favorite features of contentful which makes it very eaasy to get the specific field datas.)"
- "The content entries according to the JSON format of the animals example used earlier. This shows four entries which are being displayed on the page further."
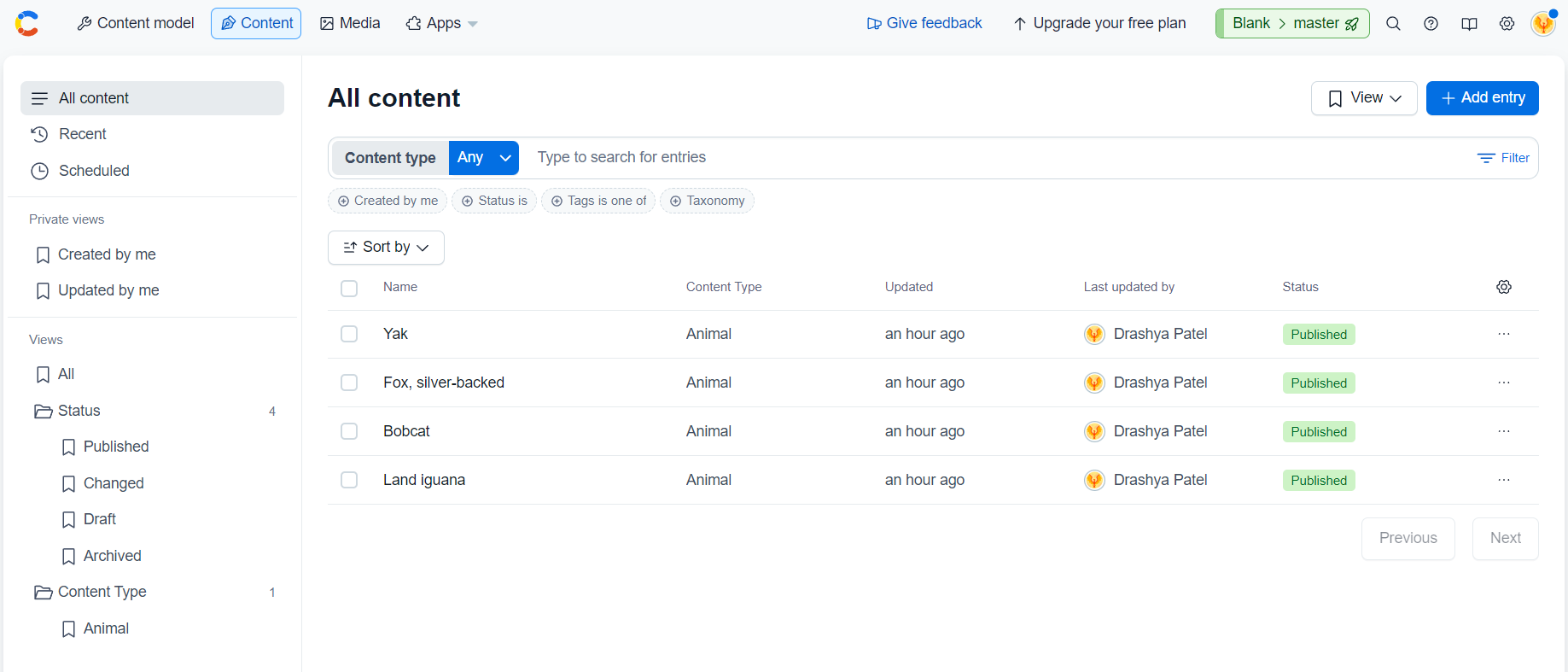
- "This is how the Contentful gives you an option to add content in your custom data fields."
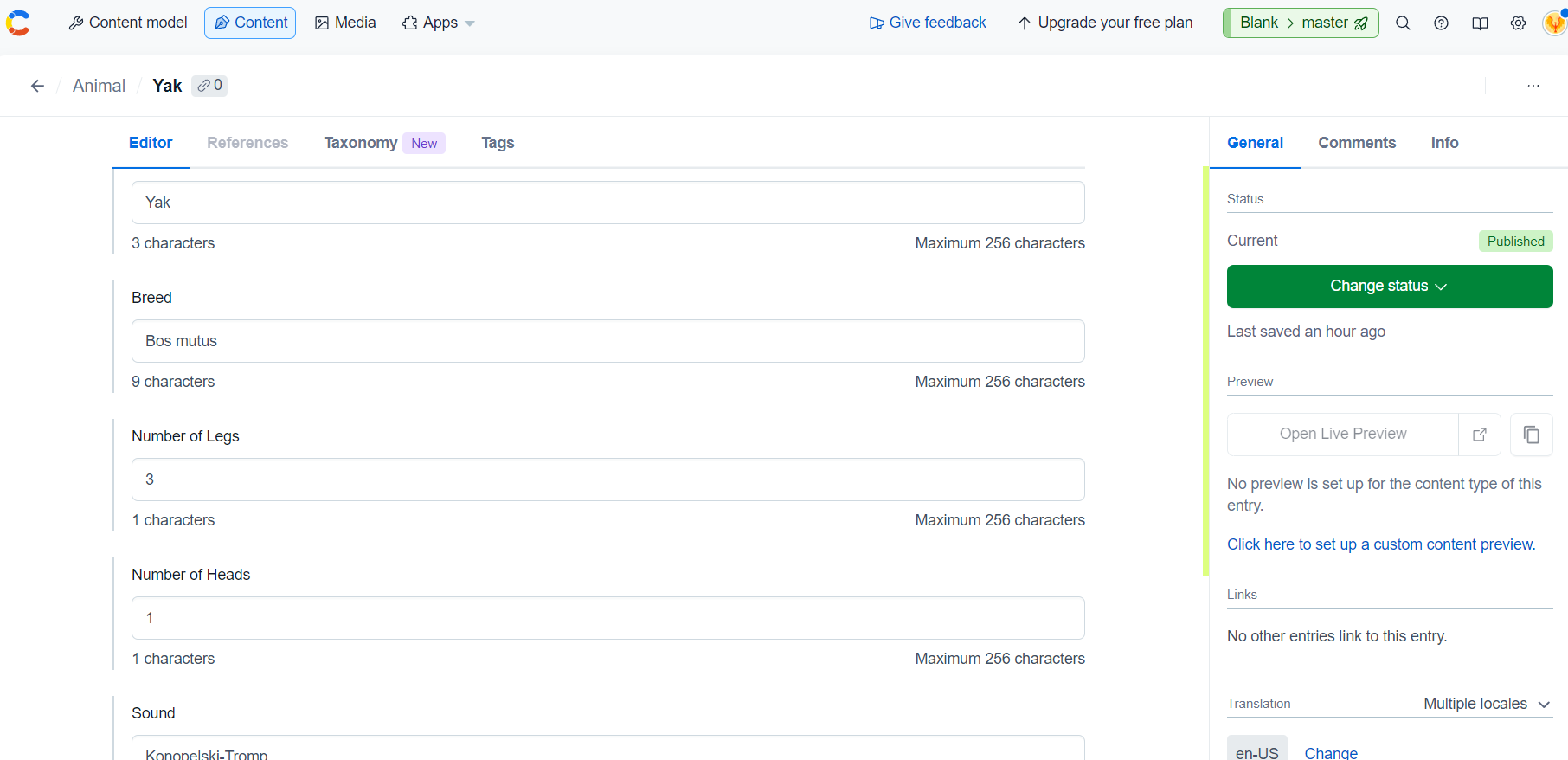
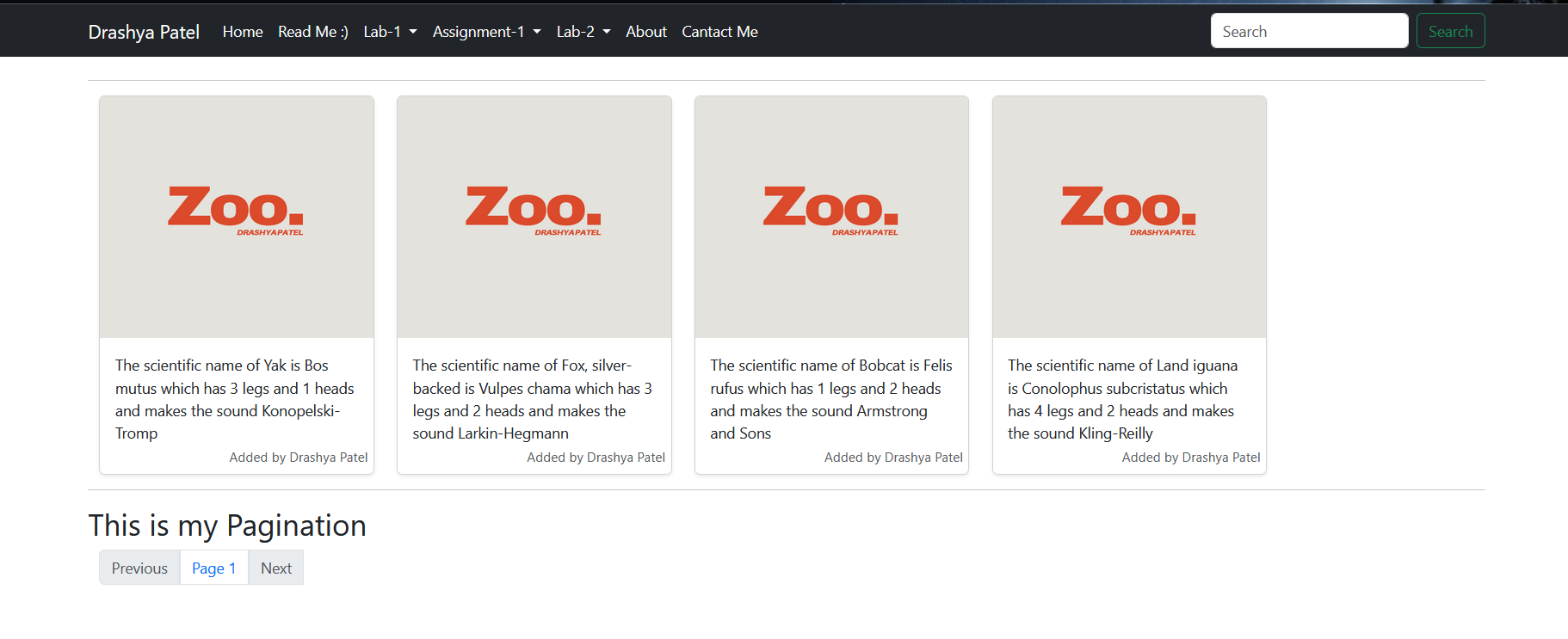
- This is how the Zoo page is looking, the content is from the entries on the Contentful cms and not from .json. By the adding the entries on Contentful CMS, this page will fetch the added entries and display it accordingly.
Implementation video link
Why using Contentful over other CMS?
-
Contentful’s API-driven approach and headless model make it a robust backend solution, particularly for developers needing content management across diverse platforms. Here’s why Contentful is technically advantageous for application development:
-
Headless CMS Flexibility By separating content management from presentation, Contentful supports a microservices-based architecture. This design choice offers scalability, flexibility, and future-proofing, allowing you to update frontends independently of the backend.
-
Custom Content Models Contentful allows complete control over content structures, making it adaptable to applications with complex data requirements. Custom content types and fields ensure structured and well-organized content, essential for highly dynamic applications.
-
High Performance Through API Use With its GraphQL API, Contentful minimizes data transfer, ensuring efficient, performance-optimized content retrieval. REST and Management APIs enable complete control over data operations, which can be integrated into custom workflows or automation tools.
-
Automated Workflows and CI/CD Compatibility Contentful’s webhook capabilities allow it to integrate seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines, facilitating automated deployments. This is especially beneficial in agile development environments where rapid content iteration and deployment are required.
-
Multi-Platform Content Distribution Contentful’s content distribution model is ideal for multi-channel applications. Content can be managed centrally and delivered across web, mobile, and IoT platforms, making it highly suitable for applications with an omnichannel strategy.
-
Customizable and Scalable Infrastructure Built on a cloud-based infrastructure, Contentful is designed for scalability, handling both small and enterprise-level data demands. This is essential for applications expected to grow in terms of content volume and distribution needs.
Strapi CMS
Strapi is an open-source, headless CMS built with Node.js, allowing developers to create custom content models, define APIs, and manage content through a user-friendly interface. Strapi focuses on flexibility and extensibility, giving developers control over data structures, user roles, and API endpoints.
Key Features
- Open Source and Self-Hosted: Strapi can be self-hosted on any server, providing full control over the Data Models and Content Structures.
- Customizable Content Models: Developers can create and modify content structures directly in the admin panel, adjusting the schemas as needed.
- Role-Based Access Control: Offers finely configured permissions for different user roles, ideal for team-based projects with varying access needs.
- GraphQL and REST API Support: Strapi generates both RESTful and GraphQL APIs automatically, enabling flexibility in data fetching.
- Extensibility and Plugin System: Strapi supports plugins for features like email, file uploads, authentication, and custom extensions.
Pros of Strapi CMS
- Flexibility and Customization: Custom content models and API configurations enable developers to adapt Strapi to specific project needs.
- GraphQL and REST API Support: Dual API options make Strapi versatile for various frontend frameworks.
- Open Source: Strapi’s codebase is fully open-source, allowing community contributions and customizable features.
- Self-Hosted Control: Hosting on your server gives control over security, data privacy, and performance.
Cons of Strapi CMS
- Requires Server Management: Self-hosting means handling infrastructure, security updates, and scaling.
- No Built-In CDN: Strapi doesn’t come with a built-in content delivery network (CDN) for assets, so more configuration is needed.
- Complex Setup for Beginners: It could be overwhelming as Strapi gives so much flexibility, espeacially for those who are new users and are unfamiliar with Node.js or API management.
Prismic CMS
Prismic is a SaaS-based headless CMS focusing on providing a flexible, API-driven content management experience. It comes with a user-friendly editor for non-technical users and an API for developers to access structured content. Prismic also offers content scheduling, slices for component-based design, and a custom-type builder for flexible content modeling.
Key Features
- Slices: Prismic's unique component-based approach to content, allowing for flexible page building with modular components.
- Content Scheduling and Previews: Enables content scheduling and previewing changes before publishing.
- Custom Type Builder: Allows users to define custom content types and fields without code, directly in the Prismic dashboard.
- Integration Fields: Supports connections to third-party services, including Shopify, YouTube, and Google Maps.
- REST and GraphQL APIs: Allows data retrieval via RESTful and GraphQL APIs, depending on frontend needs.
Pros of Prismic CMS
- Modular Design with Slices: The slice-based architecture enables reusable components, ideal for modern frontend frameworks.
- User-Friendly Interface: Easy for non-technical users to manage content, making it a good choice for content-focused teams.
- API Flexibility: REST and GraphQL APIs enable developers to choose the most suitable API for their frontend.
- Content Scheduling: Allows scheduling and previews, useful for marketing campaigns and content planning.
Cons of Prismic CMS
- Limited Customization: SaaS-based structure means less control over the backend compared to self-hosted solutions.
- Learning Curve for Slices: Prismic’s slice-based approach can be confusing initially, especially for developers new to component-based design.
- No Self-Hosting Option: As a SaaS solution, there is no option for hosting on your own server, which may be a drawback for some projects.
Sanity CMS
Sanity is a highly customizable, API-first, headless CMS that offers real-time collaboration and a unique content studio for flexible content management. With a focus on structured content, Sanity allows developers to define schemas as code and offers an open-source content studio that can be deployed and customized as needed.
Key Features
- Schema-as-Code: Sanity uses a schema language for defining content types, allowing developers to version and manage schemas with code.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Supports real-time collaboration for multiple users editing content simultaneously.
- Customizable Content Studio: An open-source, React-based studio that developers can fully customize and extend.
- GROQ Query Language: Sanity’s custom query language (GROQ) allows for highly flexible querying of content.
- Instant Previews: Real-time previews enable developers and editors to view changes as they make updates.
Pros of Sanity CMS
- Schema Flexibility: Schema-as-code provides flexibility, especially for developers who prefer defining structures programmatically.
- Customizable Studio: The open-source content studio is fully customizable, allowing you to extend or modify it as needed.
- Real-Time Collaboration: Ideal for team environments where multiple people may need to edit or review content at once.
- Powerful Query Language: GROQ allows for flexible and specific querying, making it powerful for complex data needs.
Cons of Sanity CMS
- Complex for Beginners: Sanity’s flexibility and schema-based setup can be overwhelming for new users.
- Cost Increases with Usage: Usage-based pricing can become expensive with high data or API usage.
- GROQ Learning Curve: Sanity’s custom query language, GROQ, may take time to learn, especially for those accustomed to SQL or GraphQL.
Comparison of Strapi, Prismic, and Sanity
| Feature | Strapi | Prismic | Sanity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hosting | Self-hosted | SaaS | Self-hosted or Sanity Studio as SaaS |
| Custom Content Models | Yes, schema-based with UI | Yes, custom type builder | Yes, schema-as-code |
| API Support | REST, GraphQL | REST, GraphQL | GROQ |
| Modularity | Plugin-based | Slice-based architecture | Schema flexibility and custom studio |
| Real-Time Collaboration | No | No | Yes |
| Customization | High (self-hosted, plugins) | Limited (SaaS limitations) | Very high (customizable studio) |
| Pricing | Free, self-hosted | Usage-based, SaaS | Usage-based, with free tier |
Resources
- Contentful Official Documentation
- Ghost Documentation
- Ghost on Github
- Contentful API References
- Contentful JavaScript SDK
- Contentful API
- Ghost Architecture
- How to install Ghost CMS
- How to install Contentful
- Strapi Documentation
- Prismic Documentation
- Sanity Documentation
- Strapi on GitHub
- Prismic Slices
- Sanity Studio GitHub
- Getting Started with Sanity